This is the Test Post
Content-Type: text/html; charset=”utf-8″
This is the Test Post
=
Remote Database Administrators
Remote Database Administrator
Content-Type: text/html; charset=”utf-8″
This is the Test Post
=
How to setup Oracle 12c Upgrade and Migration Hands on Lab provided by Oracle corporation. You can very well setup on your laptop and does not required any special software. I created it on my laptop and to make comfortable. I created video and uploaded. You can setup on your laptop. Will try to add more.
Issue:
When the DB Performance issue is reported, After checking found the server load is very low, CPU/IO 90+ percent free.
But many sessiones waiting on event “resmgr:cpu quantum”. From AWR report we can see “resmgr:cpu quantum” is the TOP one consuming 100% DB time
What/Why resmgr:cpu quantum :
“resmgr:cpu quantum” means a session is waiting in a resource queue, wait until resource manager assign CPU pieces to it.
The wait event resmgr:cpu quantum is a normal wait event used by the Oracle Resource Manager to control CPU distribution. The resmgr:cpu quantum only occurs when the resource manager is enabled and the resource manage is “throttling” CPU consumption.
This is due to DEFAULT_MAINTENANCE_PLAN. From 11g onwards every weekday window has a pre-defined Resource Plan called DEFAULT_MAINTENANCE_PLAN, which will become active once the related window opens. In 10gR2, DEFAULT_MAINTENANCE_PLAN is associated with WEEKNIGHT_WINDOW and WEEKEND_WINDOW.
You can confirm this using the below SQL
SQL> select name,value from v$parameter where name in (‘resource_manager_plan’,’resource_limit’)’
SQL> show parameter resource
SQL> select window_name,resource_plan,last_start_date,duration,enabled from dba_scheduler_windows;
Solution:
Note 392037.1 – Database ‘Hangs’. Sessions Wait for ‘resmgr:cpu quantum’
Note 1339803.1 Recommended Patches for CPU Resource Manager
Set the maintenance window to other time where CPU resource is available maximum
During peak time clear the resource_manager_plan to none
alter system set resource_manager_plan=” scope=both;
You can disable resource plan for specific days by following commands
execute dbms_scheduler.set_attribute(‘MONDAY_WINDOW’,’RESOURCE_PLAN’,”);
Note: The above command will disable resource plan for Monday only
1.Login as root or admin privileged user
$ mysql -u root -p password
2. Purge the Logs with log number
test$ PURGE BINARY LOGS TO “mysql-bin.0900”
The above command will purge all logs before 0900 and keep the logs 900 and above
3. Purge the logs until specific date and time
test$ PURGE BINARY LOGS BEFORE “2009-09-02 22:00:00”;
This command will purge the logs before 2nd Sep 22:00 Hrs
What is Secure Copy?
scp allows files to be copied to, from, or between different hosts. It uses ssh for data transfer and provides the same authentication and same level of security as ssh.
Basic syntax of SCP
scp source_file_name username@destination_host:destination_folder
“copy source_file_name” into “destination_folder” at “destination_host” using “username account”.
How to copy single file
$scp -p username@hostname:/u01/local/oracle/db_01/backup/<FileName> .
How to copy multiple files
To use wildcard on the remote host, we must delimit the wildcards with backslash (\)
example
$ scp -p username@hostname:/u01/local/oracle/db_01/backup/\*.dmp .
The above command will pass “*.dmp”
How to copy Entire folder
$ scp -p username@hostname:/u01/local/oracle/db_01/backup/\* .
Examples
1.1 Copy the file “foobar.txt” from a remote host to the local host
$ scp your_username@remotehost.edu:foobar.txt /some/local/directory
1.2 Copy the file “foobar.txt” from the local host to a remote host
$ scp foobar.txt your_username@remotehost.edu:/some/remote/directory
1.3 Copy the directory “foo” from the local host to a remote host’s directory “bar”
$ scp -r foo your_username@remotehost.edu:/some/remote/directory/bar
1.4 Copy the file “foobar.txt” from remote host “rh1.edu” to remote host “rh2.edu”
$ scp your_username@rh1.edu:/some/remote/directory/foobar.txt \
your_username@rh2.edu:/some/remote/directory/
1.5 Copying the files “foo.txt” and “bar.txt” from the local host to your home directory on the remote host
$ scp foo.txt bar.txt your_username@remotehost.edu:~
1.6 Copy the file “foobar.txt” from the local host to a remote host using port 2264
$ scp -P 2264 foobar.txt your_username@remotehost.edu:/some/remote/directory
1.7 Copy multiple files from the remote host to your current directory on the local host
$ scp your_username@remotehost.edu:/some/remote/directory/\{a,b,c\} .
Latest Gartner Magic Quadrant Data Integration Tools report for 2016.
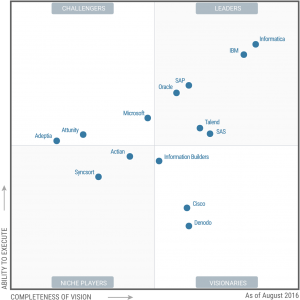
Details of the report you can get it by request in the Gartner home page or Informatica
We can use simple linux commands to rotate logs. There are some tools also available to rotate the logs.
Method 1: Backup the log and make the log empty without stopping the service.
1.1 Backup the current Log
$ tail -100000 alert_UPGR.log > alert_UPGR.log.bak
$ ls -ltr alert_UPGR.log*
-rw-r—– 1 oracle oinstall 353665 Jul 4 00:41 alert_UPGR.log
-rw-r–r– 1 oracle oinstall 353665 Jul 4 00:52 alert_UPGR.log.bak
1.2 Compress the backed up Log
$ gzip alert_UPGR.log.bak
$ ls -ltr alert_UPGR.log*
-rw-r—– 1 oracle oinstall 353665 Jul 4 00:41 alert_UPGR.log
-rw-r–r– 1 oracle oinstall 33727 Jul 4 00:52 alert_UPGR.log.bak.gz
1.3 Empty the active log
$ >alert_UPGR.log
$ ls -ltr alert_UPGR.log*
-rw-r–r– 1 oracle oinstall 33727 Jul 4 00:52 alert_UPGR.log.bak.gz
-rw-r—– 1 oracle oinstall 0 Jul 4 00:53 alert_UPGR.log
1.4 Confirm the alert log is updated
SYS@UPGR:SQL> alter system switch logfile;
System altered.
SYS@UPGR:SQL> exit
$ ls -ltr alert_UPGR.log*
-rw-r–r– 1 oracle oinstall 33727 Jul 4 00:52 alert_UPGR.log.bak.gz
-rw-r—– 1 oracle oinstall 229 Jul 4 00:54 alert_UPGR.log
2. How to rotate Catalina.out log when it is more than 5M?.
2.1. Create this file
/etc/logrotate.d/tomcat
2.2. Copy the following contents into the above file
/var/log/tomcat/catalina.out { copytruncate daily rotate 7 compress missingok size 5M }
About the above configuration:
Make sure that the path /var/log/tomcat/catalina.out above is adjusted to point to your tomcat’s catalina.out
daily – rotates the catalina.out daily
rotate – keeps at most 7 log files
compress – compressesthe rotated files
size – rotates if the size of catalina.out is bigger than 5M
We need sometime run the script in background
1. How to execute the script in Background
Let us say you have created script call test_bg.sh
Login to remote host with appropricate username and password
Syntax
$ nohup <scriptname> > <logname> &
Example:
$ nohup /home/oracle/mudhalvan/scripts/test_bg.sh > /home/oracle/mudhalvan/scripts/test_bg.log &
2. How to check any background jobs are running in this session
$ jobs
3. Test with example
oracle@localhost:~/mudhalvan/scripts$ cat test_bg.sh
find /. -name “test” -print
oracle@localhost:~/mudhalvan/scripts$ ls -ltr test_bg.sh
-rwxr-xr-x 1 oracle oinstall 29 May 27 19:43 test_bg.sh
oracle@localhost:~/mudhalvan/scripts$
oracle@localhost:~/mudhalvan/scripts$ nohup /home/oracle/mudhalvan/scripts/test_bg.sh > /home/oracle/mudhalvan/scripts/test_bg.log &
[1] 3865
oracle@localhost:~/mudhalvan/scripts$ jobs
[1]+ Running nohup /home/oracle/mudhalvan/scripts/test_bg.sh > /home/oracle/mudhalvan/scripts/test_bg.log &
oracle@localhost:~/mudhalvan/scripts$
4. Why we need to run the scripts in background
1. You may be connected remotely to the server and execute some script which need to be executed for more than few hours. Due to network issue or session security you remote session may disconnect which may cause your running script end at half way.
2. Long running script which will not take your one session of your remote client connection from your client machine.
5. Benifits of running a script in background
1. Disconnect or network disturbance on your remote client will not impact your script execution
2. You can use the current remote session for another process
Many of us facing problem now once our PC is automatically upgraded to Windows 10. We feel uncomfortable with Start button and the Desktop screen. I also faced the same and below steps to helped to change the Start screen.
1. Click the Start button
2. Click the Settings command.
3. At the Settings window, click the setting for Personalization.
4. At the Personalization window, click the option for Start.
5. In the right pane of the screen, you’ll see a setting that says “Use Start full screen” that’s currently turned off. Turn that setting on so the button turns blue and the setting says “On.
Now click the Start button, and you should see the full Start screen.